Organic traffic drop can be frustrating and even destructive to your business, especially if search engines are your primary traffic source.
In this article, we will identify the most common reasons for the decline in organic traffic, and also learn how to restore it.
Google algorithm update
Google updates its algorithm a few times per year. Such an update can result in anything from a slight drop in organic traffic to the loss of most search traffic.
Some updates may negatively impact only sites in certain industries (e.g. financial or healthcare).
Recommended action: check a list of Google Search ranking updates. This will help you identify correlations between the update timing and website traffic loss.
However, there are no specific guidelines on how to recover from Google algorithm updates. Google only recommends following the guidelines on how to create helpful content.
Also, keep in mind that even if improvements made to the site are correct, your organic traffic may not recover until the next broad algorithm update is released.
AI Overviews
Google has many search result features: featured snippets, related questions, knowledge cards, OneBox results, etc.
However, the recently launched AI overviews are having a particularly negative impact on organic traffic. If Google displays AI overviews for your target search queries, it will most likely result in fewer clicks. The reason is that users can get the necessary detailed information directly from the search results:
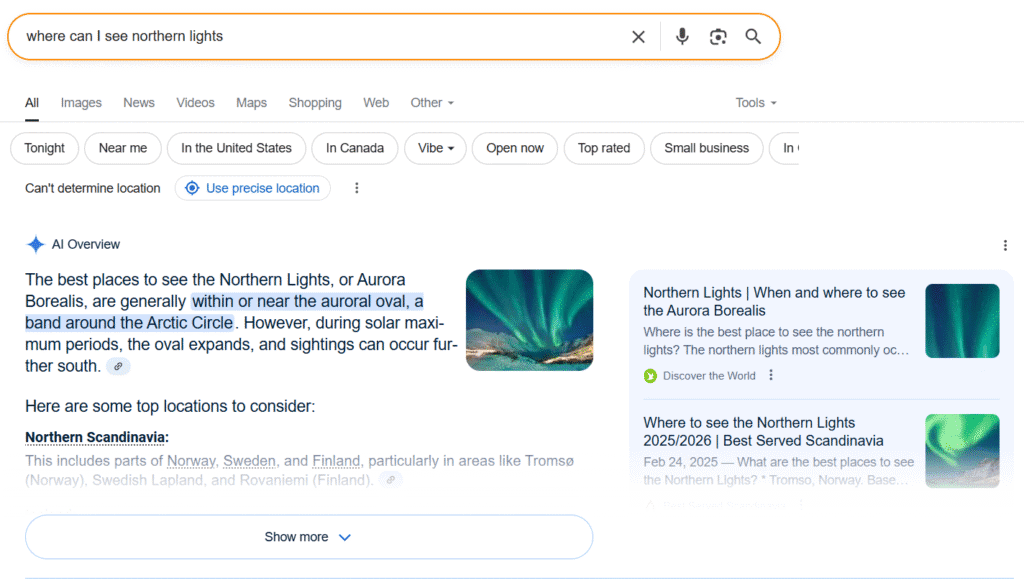
Recommended action: try to target search queries that don’t trigger AI overviews. Google now shows them in about 15-20% of searches, so they can still be avoided.
If you can’t avoid AI overviews, your content should include information beyond what is shown in the AI overview.
The vast majority of AI overviews are text-based, so you can include more images and especially videos in your content. This will give users more reasons to visit your page rather than just read an AI overview.
Incorrect directives in your robots.txt file
Directives that disallow crawling of the entire website (such as Disallow: / ) are frequently used in the robots.txt file of a staging domain (subdomain).
However, sometimes developers forget to remove such directives from the robots.txt file when launching a new website. This blocks search engines from crawling the new site, causing organic traffic to drop sharply.
Recommended action: check your robots.txt file and make sure it does not contain directives that restrict the crawling of the entire site or its important sections.
Misplaced ‘noindex’ directive
You can accidentally add the 'noindex' directive to either the meta tag or the ‘X-Robots-Tag’ HTTP header of the entire website or its key pages.
As a result, pages are not indexed and do not appear in search results, which leads to a sharp drop in organic traffic.
Recommended action: check if pages have the 'noindex' meta tag. In the page source code, this meta tag looks like this:
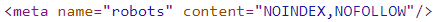
In the ‘X-Robots-Tag’ HTTP header, the 'noindex' meta tag looks as follows:
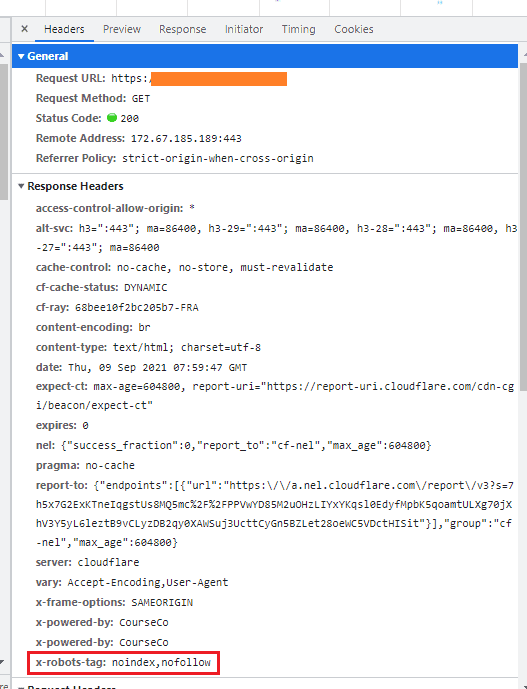
You can check the HTTP header of a page in your Search Console or using online tools like this one.
Change in the URL structure without 301 redirects
Google cannot attribute the ranking signals from old URLs to new ones without redirects between them.
So if you change the URL structure of your website, you need to redirect old URLs to the new ones using 301 redirects. Otherwise, your website will lose its rankings and search traffic.
Recommended action: ensure your most important old URLs are redirected to the relevant new URLs using permanent 301 redirects. This includes pages with many backlinks, internal links, and those that generate a lot of organic traffic.
Avoid using meta refresh redirects or other client-side redirects for permanently moved URLs.
Lost backlinks
The quality and quantity of backlinks is one of the most important ranking factors. If backlinks are lost, the website will almost certainly lose its rankings.
There are various reasons why a website may lose backlinks, such as changing URLs without 301 redirects, etc.
Recommended action: conduct a backlink audit to check if you’ve lost backlinks. If you find lost or broken backlinks, restore pages that have backlinks, or redirect the removed pages to relevant existing pages.
Incorrect canonical links
Canonical links must point to URLs that return the 200 HTTP status code (“OK”). Canonical URLs should also not be blocked from crawling in the robots.txt file.
Incorrect canonical links may point to “Not found” pages, redirected URLs, staging domains (subdomains), and so on.
Recommended action: make sure canonical links are correct in the rel=canonical tag or the HTTP header. Otherwise, important pages on your site may be de-indexed and you will lose organic traffic.
Bad server or web hosting
If your server does not respond to crawl requests or the response time is too long, Google may stop crawling and indexing pages on your site. As a result, your site will not be fully indexed, which will most likely lead to a drop in organic traffic.
This problem may occur after a site migration when the load on the server increases as it has to handle requests to both old and new URLs.
Another possible reason for this problem is a bad hosting plan or hosting provider – I experienced this problem first hand.
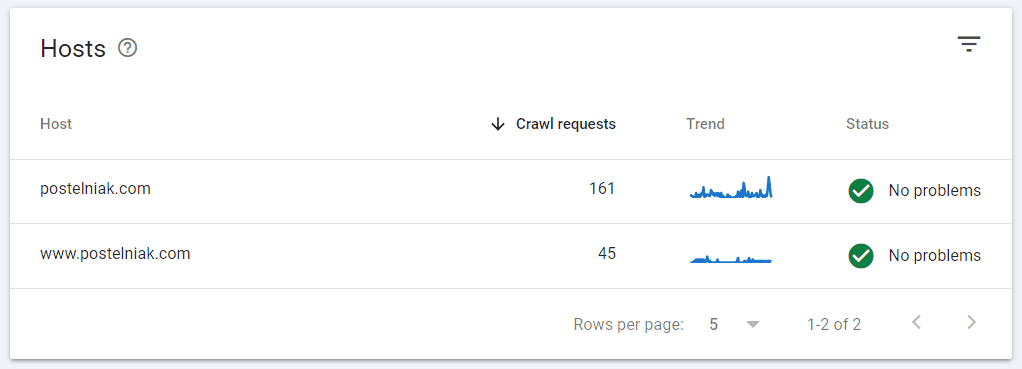
Recommended action: check if Google encountered any problems while crawling your site. Go to Search Console and review the Crawl Stats report (section “Settings”). If everything is fine, you’ll see something like this:
If there are any problems, you will see something like this:
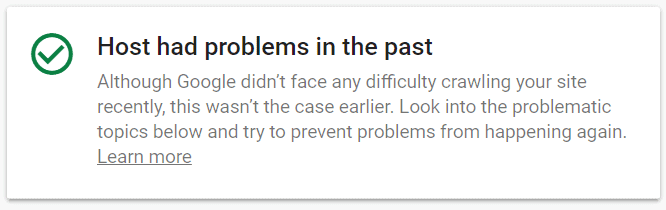

Pay also attention to the crawl requests reports. If you notice that many crawl requests resulted in “Page timeout”, “DNS unresponsive”, “Fetch error” or another similar issue, this is a sign that there are problems with your server.
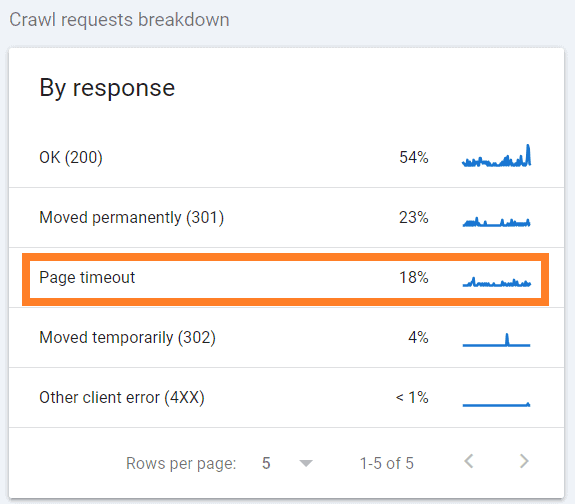
You need to ensure server uptime is close to 100% and minimize server response time. This may include various actions such as improving site speed, upgrading your hosting plan, or even changing your hosting provider. A good server response time is 200ms or less.
Lots of indexed pages with low value
“Low value” pages are pages that have little to no value to users and search engines, for example:
- duplicate pages
- internal search results
- empty faceted navigation pages
- expired job postings, events, etc.
- various archive pages, tags, etc.
Often such pages are automatically generated by your content management system, and you might not even know they exist.
A large number of low-value pages on your site can negatively impact the search visibility of other, more valuable content.
Recommended action: delete or add the 'noindex' meta tag to low-value pages to exclude them from search results.
Recent changes on the website
Sometimes fixes aimed to make the website better, such as removing old content or adding new functionality, may hurt SEO.
This can be the case if your website improvements result in lost backlinks or technical SEO issues.
For example, by adding internal search functionality, you might end up with thousands of indexed internal search results pages.
Recommended action: it depends on the changes made to your site. You will likely need to consult with an SEO specialist to identify the problem and create a plan to recover search traffic.
Quality of website content
High-quality content needs to be original, easy to read, and cover the topic in detail. Good articles are also up-to-date and often have many social media shares.
If your content is generating less organic traffic, it may be outdated, articles may be missing important subtopics, etc.
Recommended action: conduct a detailed content audit. Delete outdated articles, consolidate articles on the same topic, and update your best articles.
Blocking or redirecting users from certain locations
This may occur on international websites that have sections intended for users from certain countries.
Recommended action: first, do not redirect all US users (including Googlebot) strictly to the US version/section of your site. This may prevent Google from crawling, indexing, and ranking other sections of your site.
Second, use banners instead of forced redirects:

It is also possible that your server is blocking access to the site from specific countries. If you are doing this on purpose, you may want to reconsider this decision.
Updated titles and meta descriptions
If you’ve recently updated titles and/or meta descriptions on key pages, this also may cause your organic traffic to decline.
Lower click-through rates (CTR) on new titles and descriptions can result in lost traffic, even if your rankings have not changed.
Recommended action: check your top-performing pages and make sure they have optimized titles and meta descriptions.
Your competitors
The world of digital marketing is highly competitive, especially when it comes to search engine optimization. If you don’t rank first, your competitors will.
Your competitors may be simply gradually overtaking you and taking over your positions in search results. They won’t be able to outrun you in a day or a week, so in such cases, organic traffic declines gradually.
Recommended action: to outrank competitors, ensure your content is more comprehensive and easier to read than theirs.
At the same time, work on improving your site’s domain authority so search engines will consider your content more credible by default.
Seasonality
If your business is seasonal, you may see a decline or rise in traffic as the seasons change.
For example, if you sell warm clothes, your organic traffic is likely to drop by summer and increase by winter.
Recommended action: use the low season to implement as many SEO best practices as possible. This will help you attract more visitors to your site when the high season arrives.
Change in search behavior
Some topics simply lose relevance over time. For example, people are less likely to search for old smartphones, cars, movies, etc. This results in lower search volumes and hence traffic.
Recommended action: you can use Google Trends to check if the topics you write about are still interesting to people.
Too many ads on the site
There is nothing wrong with displaying ads on the site but too many ads is another possible reason for organic traffic drop.
Google may apply an algorithmic penalty if your ads make it difficult for users to access page content. Ad displaying practices that may cause an algorithmic penalty include but are not limited to:
- auto-playing video ads that follow you down the page;
- using various types of sticky and full-screen banners;
- high ad density;
- using wordiness and/or one-sentence paragraphs just to make the page longer and display more ads.
Recommended action: avoid the above and similar questionable practices of displaying ads. You can also review this guide that explains how to effectively display ads without negatively impacting site speed and ad revenue.
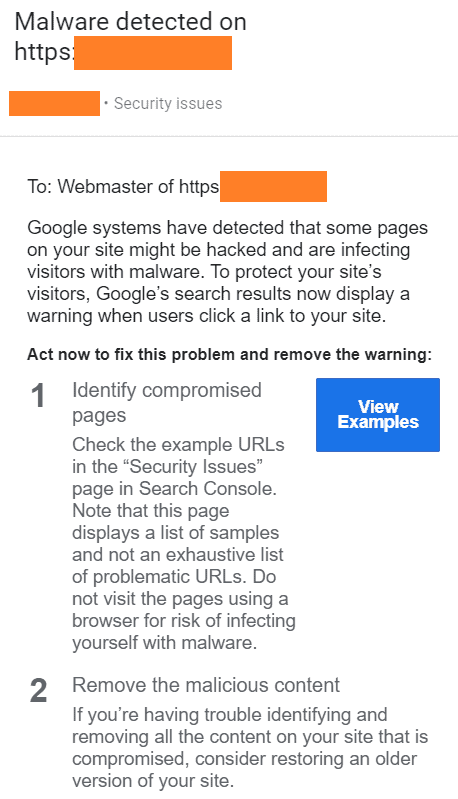
Security issue
Security warnings appear next to your site in search results, even if it’s not removed from the search. If a security issue is detected on your website, the affected pages appear on Google as follows:

Such security warnings can scare people away, causing your organic traffic to plummet.
Recommended action: you’ll receive a notification in Google Search Console with details about the security issue and the necessary actions to resolve it, for example:
Manual action
If Google takes manual action against the entire website or its individual pages, you’ll receive a notification in Google Search Console with details about the manual action, for example:
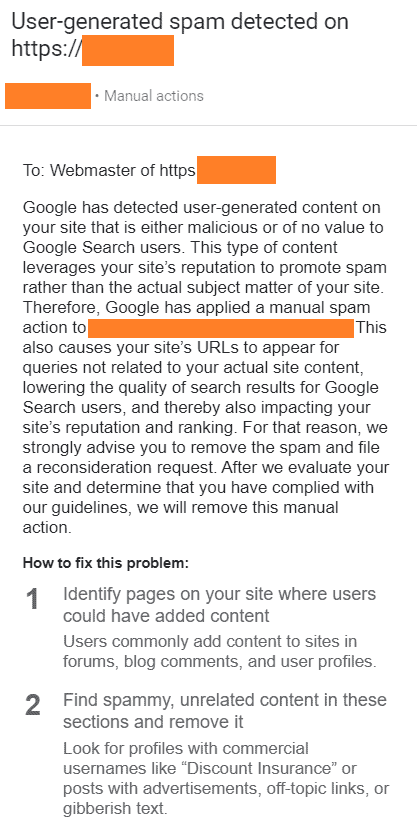
Google may issue manual action against a website for many reasons. When Google takes such actions, websites can disappear from search results or significantly drop in rankings.
Recommended action: you’ll find all the necessary information about the manual action and how to remove it in Search Console. But remember that removing Google’s manual actions can take a lot of time and effort.
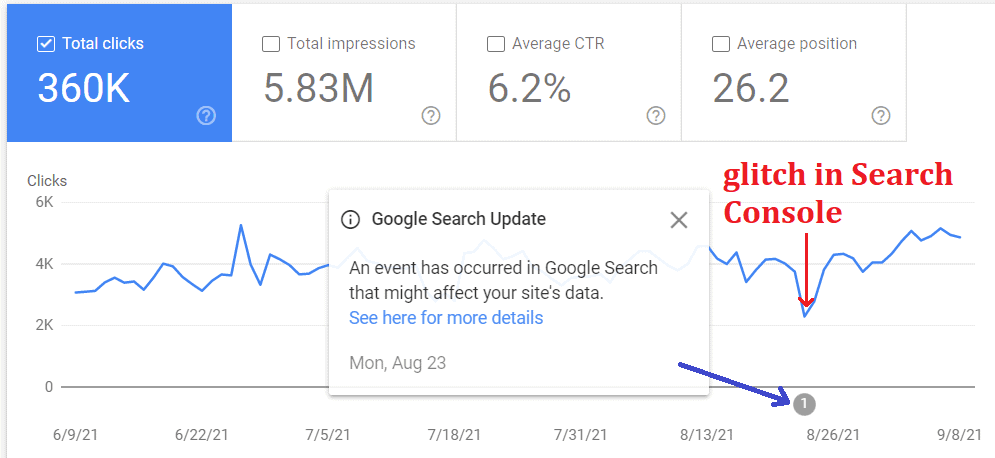
Glitches in Google Search Console or Google Analytics
Finally, everything may be fine, and the organic traffic drop can be due to a temporary glitch in the reporting tools.
Recommended action: check your Google Analytics and make sure the tracking ID and global site tag are set up correctly. Then check Google Search Console for data anomalies flagged in the Performance report:
Conclusion
A drop in organic traffic can be caused by a variety of reasons, and it is not always easy to determine the exact cause. In some cases, multiple causes are combined, resulting in a cascade effect.
I hope this article will help you identify the causes and recover your organic traffic.
