In this article, I’ll debunk the most common SEO myths that have been circulating for years.
Search algorithms and digital marketing in general are constantly changing. Relying on misconceptions about search engine optimization may waste a lot of time and resources.
Let’s clear up the most common SEO myths so you can use effective strategies to boost your website’s search visibility.
Site Speed (Core Web Vitals) is a Major Ranking Factor
This is probably the most common SEO myth I encountered in my practice. Many SEOs often cite poor website speed as the number one problem that needs addressing to improve SEO.
This myth has its roots in the blog posts where Google confirmed that it uses site speed in web and mobile search ranking.
In 2010, Google confirmed that site speed is a ranking factor. However, they noted that site speed “doesn’t carry as much weight as the relevance of a page”.

In 2018, Google confirmed that site speed affects mobile search ranking. They said it “will only affect pages that deliver the slowest experience to users”.

With the introduction of Core Web Vitals, this myth has become even more common.
Improving Core Web Vitals can help your rankings and improve user experience. However, they are just a “tie-breaker” in the ranking system for pages with equally good content.
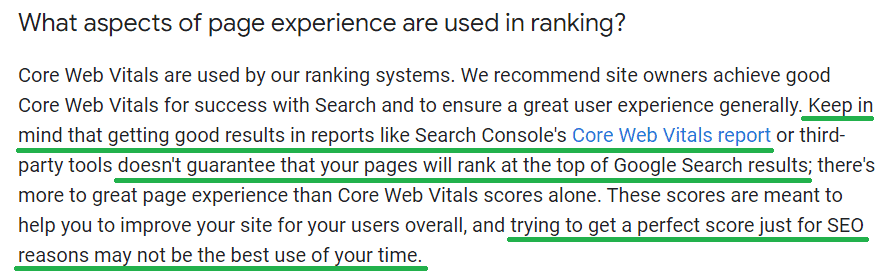
Therefore, while site speed affects search engine rankings, it is not the primary but a minor ranking factor.
E-A-T (E-E-A-T) is a Direct Ranking Factor
Google first talked about E-A-T, which stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, in 2014. This was in its Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines.
However, everyone started talking about E-A-T in August 2018. This was after the well-known Google “Medic” algorithm update. The update negatively impacted many sites in the “Your Money Your Life” industries.
Since then, many SEOs have believed that E-A-T is a direct ranking factor.
E-A-T, which later changed to E-E-A-T (adding “Experience”), is important for building trust with users. However, it is not a direct ranking factor in the traditional meaning.
This is a concept used by human reviewers hired by Google. They check the overall quality of Google Search results. Google’s engineers then take these evaluations into account when updating the ranking system. So E-A-T is not a metric that search engines directly use to determine rankings.

Certainly, your content should be authoritative and trustworthy, and the author should demonstrate experience and expertise.
Showing strong E-E-A-T is more than just adding a Contact Us, About Us, and author bios to the website.
The key point is that users must trust your content. It should be written and reviewed by experts with the necessary experience in the subject matter.
You Need More Backlinks to Rank Higher
One of the oldest SEO myths is that the quantity of backlinks directly correlates with higher search engine rankings.
I must admit that earlier (15 years ago), the number of backlinks was one of the most important ranking factors. At that time, having many low-quality backlinks could help a page rank higher in search results.
However, search engine algorithms have evolved significantly and have become more sophisticated in evaluating the quality and relevance of backlinks.
Now, it’s more important to get high-quality backlinks from trusted and relevant websites. The quantity of backlinks is not as important as their quality.
Of course, a website needs backlinks to get off the ground and rank in search results for relevant search queries. However, modern link building is not about the number of backlinks, but the quality and relevance of those links.
Word Count is a Ranking Factor
Another SEO myth is that longer articles always rank better in search engine results.
The roots of this common SEO misconception likely lie in a 2015 study that found that long-form content ranks well.
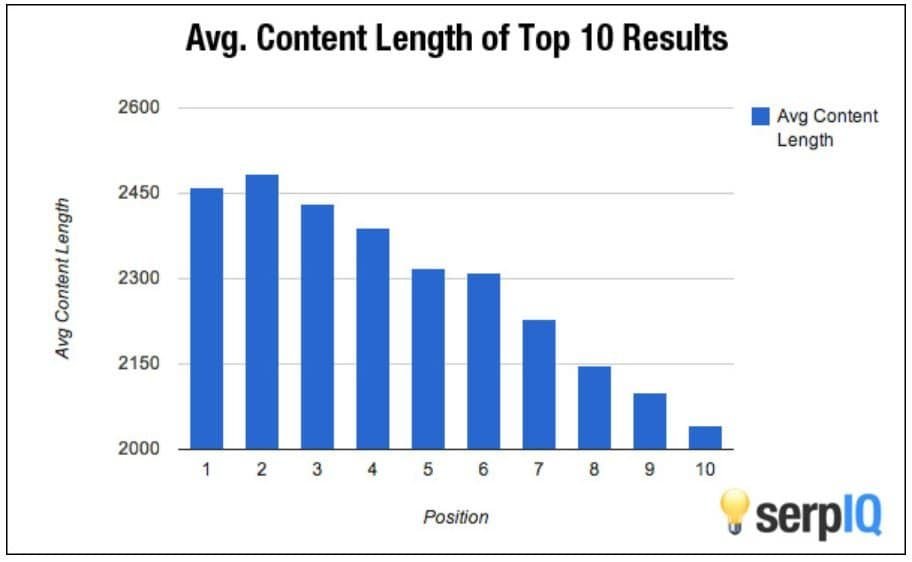
After this study, many SEOs became focused on publishing “comprehensive guides” that are “at least 2000 words.” This happened even for simple topics, like how to boil eggs.
Many SEO content writers now add extra words or unnecessary details to their articles. They do this to reach the “minimum threshold” of 2000+ words.
Longer content can indeed provide more in-depth information and potentially attract more backlinks. However, word count itself is not a direct ranking factor.
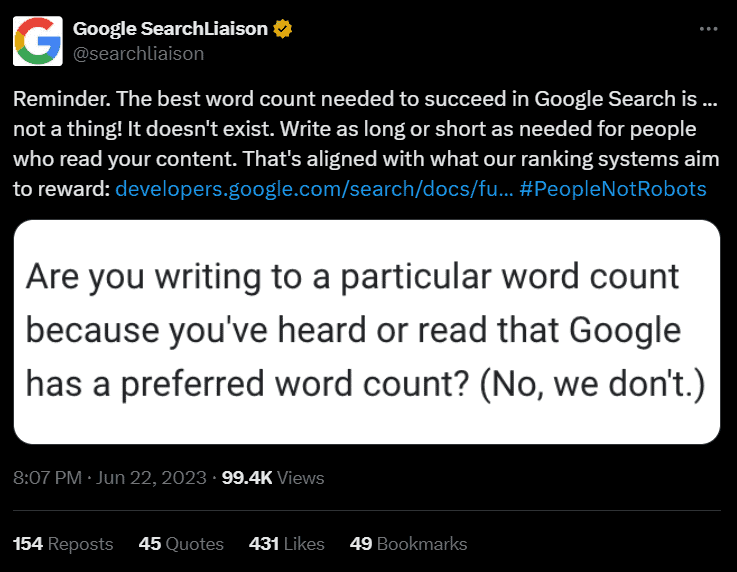
The truth is that your content should be comprehensive, meaning it should cover the topic in detail. Sometimes it takes 5000 words, sometimes 500 words.
The length of your article doesn’t determine its quality or search ranking. A shorter article can still be comprehensive and rank well.
There is an ideal keyword density
The concept of ideal keyword density is a well-known SEO myth that has persisted since the early 2000s. You may have heard about various percentages. Some suggest that the ideal keyword density is 1%, while others recommend 2.5%, and still others advise no more than 5%.
The truth is that there is no ideal keyword density. Indeed, your content should include your target keywords so that Google can understand what your page is about. But keywords should be used naturally and contextually, where they make sense.
You don’t need to add keywords where they are irrelevant just to achieve X% density. Instead of focusing on keyword density, you need to focus on semantic and topical relevance. This involves using related terms, synonyms, and long tail keywords that allow you to describe the topic in detail.
At the same time, keyword stuffing isn’t a good SEO practice and can seriously harm your page’s ranking.

Keyword stuffing can lead to penalties, demotion in search results, or even de-indexing of your page.
Therefore, add your focus keyword to the page title, H1 tag, and mention it in the body copy where appropriate. For better on-page optimization, also include related keywords throughout the body copy and in H2 headings.
Social Media Signals Directly Influence Search Rankings
Many still believe that a high number of social media likes and shares improves search rankings, but this is another SEO myth.
Social media KPIs can be valuable, but they are not used for rankings.
However, social media can indirectly influence SEO through increased website traffic and brand awareness. Engaging content shared on social media can attract more visitors to your website. This can potentially lead to an increase in the number of backlinks that search engines take into account.
Therefore, creating viral content that blows up social media may help you indirectly improve your search engine visibility.
Duplicate Content Penalty
The statement that duplicate content will result in a penalty from search engines is one of the most ingrained SEO myths.
Indeed, your website won’t rank high if you simply copy content from websites that already rank high for your target search terms. Search engines are smart enough to determine the original version of the content to display in search results.
However, many SEOs and website owners still believe that duplicate content within a website can result in a penalty. This is not true – there is no special penalty for duplicating content.
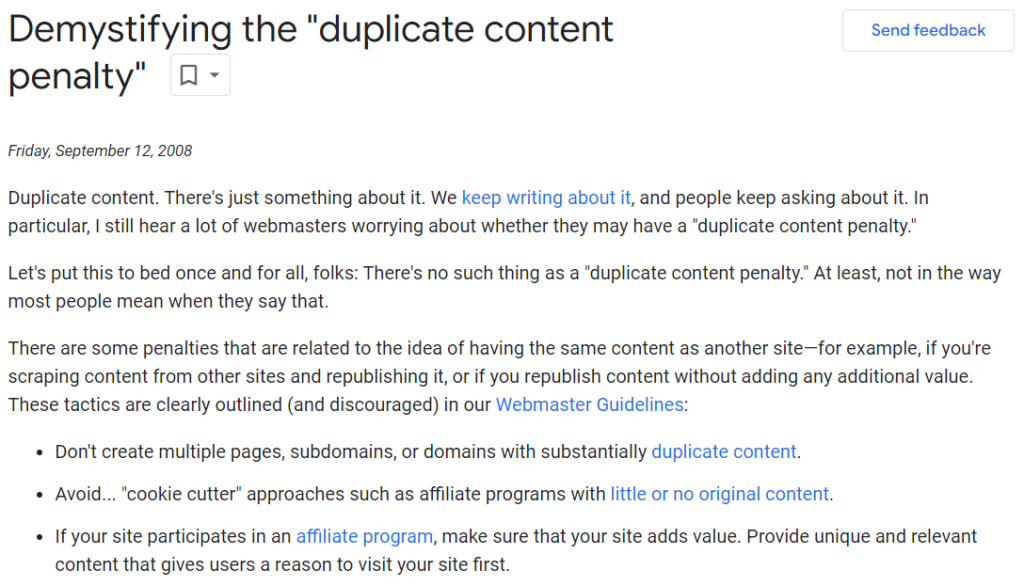
If you have duplicate pages on your website, search engines will choose one version (canonical) for indexing and ranking. The rest will be ignored, and your site will not be penalized.
However, be aware that spam techniques that involve duplicate content, such as scraped content, violate Google’s guidelines. If you engage in this practice, your website can be penalized.
Fresh Content Ranks Better
Many believe that publishing fresh content is necessary to boost a site’s search rankings.
The fact is that Google shows users the most relevant and high-quality content. This means that both fresh and evergreen content can rank well depending on the topic.

For example, if you have an article about the “Best Movies of This Year,” update it regularly. This way, your list will include all the new movies worth watching.
If you have an article on a topic like “How to tie shoelaces,” you don’t need to update it often. This topic has not changed much over the years.
Another variation of this SEO myth is that you must constantly publish new content to maintain search rankings. Once again, it’s not about the freshness, but the quality of published articles.
Instead of focusing solely on quantity, prioritize creating high-quality content that covers the topic in depth.
Local SEO is Easier than Traditional SEO
Some clients and even SEOs believe that local SEO is easier than traditional SEO. The main reason for that is that you have a lower number of direct competitors in local SEO.
So, for example, a local dentist should only compete with other local dentists, not with all dentists in the country. This can create the illusion that the competition is less intense and therefore the work is easier.
But in practice, local SEO is not easier than traditional – it’s just different. While the number of competitors may be smaller, the competition within that group can be intense. In some cases, local SEO may be even more complex, especially for businesses with multiple locations.
To succeed in local SEO, you need to manage not only your website, but also your Google Business Profile. You also need to manage reviews that you don’t control and that may harm your business.
Local SEO requires you to work with different platforms and also focus on your local community. This can be just as challenging as traditional SEO, which focuses more on keywords and creating content.
SEO is a Quick and Easy Job
Many website owners, CEOs, and developers think SEO is a quick and easy task. They believe it can be done overnight.
They think some quick fixes, such as optimizing meta tags, will quickly boost their website’s ranking on search engine results pages. However, this is another misconception.
SEO is not a one-time task – achieving long-term success in SEO requires a sustained and ongoing effort.
Effective SEO requires a strategic approach to optimizing your website. It takes some time and effort to implement properly, and the results are not immediate.
So instead of looking for quick fixes, invest in long-term strategies that show a much greater ROI.
Conclusion
Believing in misconceptions can lead to wasted time and resources, and not just in SEO. Separating fact from fiction allows you to focus your SEO efforts on decisions that yield tangible results.
I hope this article gives you a competitive edge by helping you avoid common SEO myths.
If you want to learn more ways to increase your organic traffic, check out these proven SEO tips.
